Risk ManagementSustainability
Fundamental Approach and Issue Awareness
JERA strives for effective risk management by understanding the risks associated with our corporate activities and minimizing losses when these risks materialize. These efforts support our goal of enhancing corporate value and fulfilling our social responsibility to stakeholders.
Potential risks that could have a significant impact on our corporate activities include market risks (commodities, foreign exchange, and interest rates); risks of policy changes, particularly in energy and environmental policies; business investment risks, including operational accidents, damage to facilities due to natural disasters, shutdowns, or construction delays; compliance risks; and threats such as cyberattacks and malware affecting power plant control systems and other critical infrastructure.
In addition, geopolitical risks arising from heightened political and social tensions between countries and regions, such as the situation in Russia and Ukraine and US-China relations, must be appropriately addressed in the same manner as country risk.
The JERA Group is committed to the continued enhancement of our risk management to fulfill our social responsibility as an energy company that supports social infrastructure.
Risk Management System
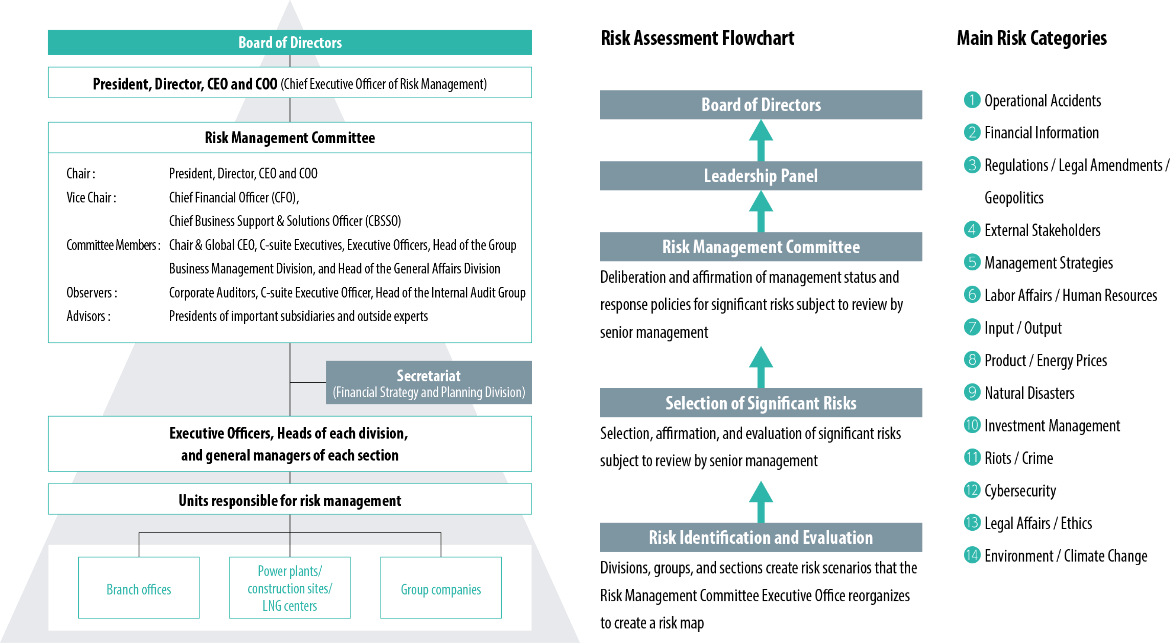
We have established a highly effective risk management system headed by the company President, Director, CEO and COO to ensure a stable energy supply and fulfill our social responsibilities.
In non-emergency situations, our fundamental approach to risks associated with our business activities is to manage them within the execution of duties by the unit responsible for the operations. When the risk affects multiple divisions, we manage it appropriately in a cross-organizational manner. In the event of a crisis, an emergency task force headed by the company President, Director, CEO and COO is deployed to respond quickly and appropriately to minimize the impact on our business.
In addition, the Financial Strategy and Planning Division, which serves as the risk management division at JERA, is organizationally and structurally independent from each division that conducts business, contributing to healthy tension within the system.
The Risk Management Committee, chaired by the company President, Director, CEO and COO, meets quarterly and is attended by several parties to ensure appropriate monitoring of risks (see Risk Management Structure below). These include the C-suite executives or officer in charge of each division, corporate auditors, and the Internal Audit Group, among others. In particular, we strive to prevent risks from materializing by reporting on our policies and specific measures for dealing with risks that could significantly impact our business. In the unlikely event that a risk materializes, the necessary reports on the response of the emergency task force are provided quarterly.
Discussions at the Risk Management Committee are reported to the Leadership Panel and the Board of Directors each time, reflecting the opinions of executive officers, directors, and outside directors.
In addition, all outside directors receive an explanation of the company's risk management system and methods upon appointment, and their opinions are incorporated through exchanges of views and other means.
Risk Management Structure(as of July 31, 2024)
Highly Effective Risk Management
Our approach to risk management is based on combining the functions of integrated risk management, evaluation of financial soundness, and evaluation of individual investments.
Integrated Risk Management
Integrated risk management defines and classifies the risks we face into three categories: operational risk, market risk, and credit risk. We quantify our total risk exposure based on market risk and credit risk.
The difference between total risk exposure and risk capital is calculated as the risk buffer.
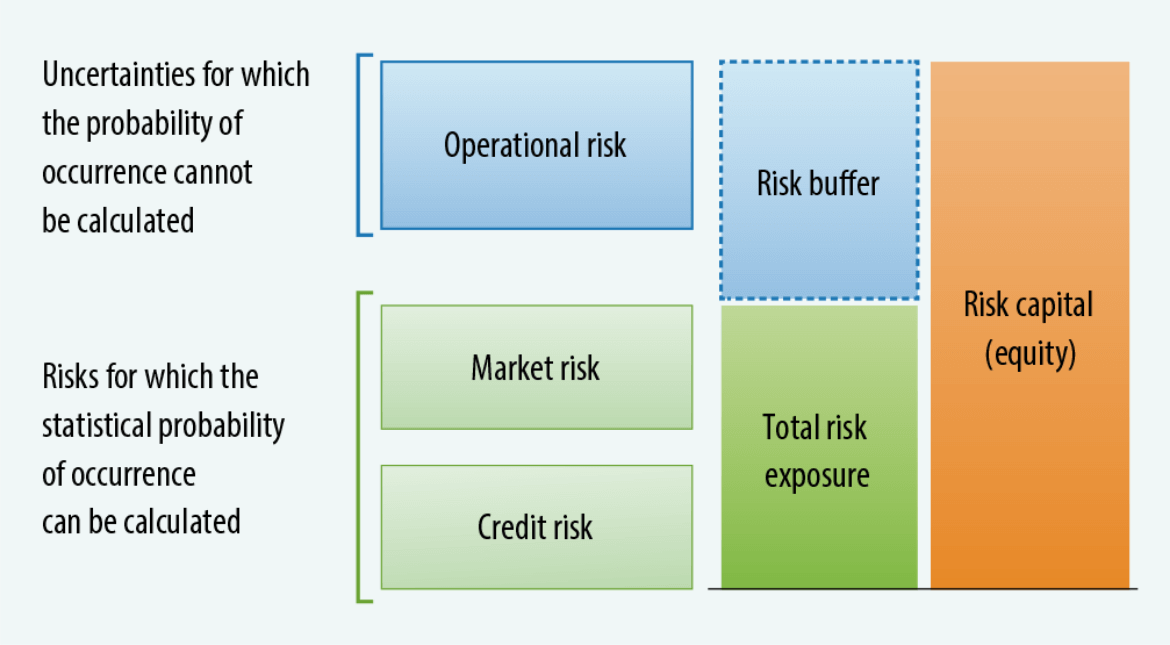
Our risk buffer is maintained at a certain level by considering operational risk as an uncertainty for which the probability of occurrence is incalculable. Operational risk is managed using a risk map that impacts management activities on the vertical axis and the frequency of risk occurrence on the horizontal axis. For each managed risk, we take measures such as retention, mitigation, and transference in cooperation with each division and the Financial Strategy and Planning Division, depending on the type and characteristics of the risk.
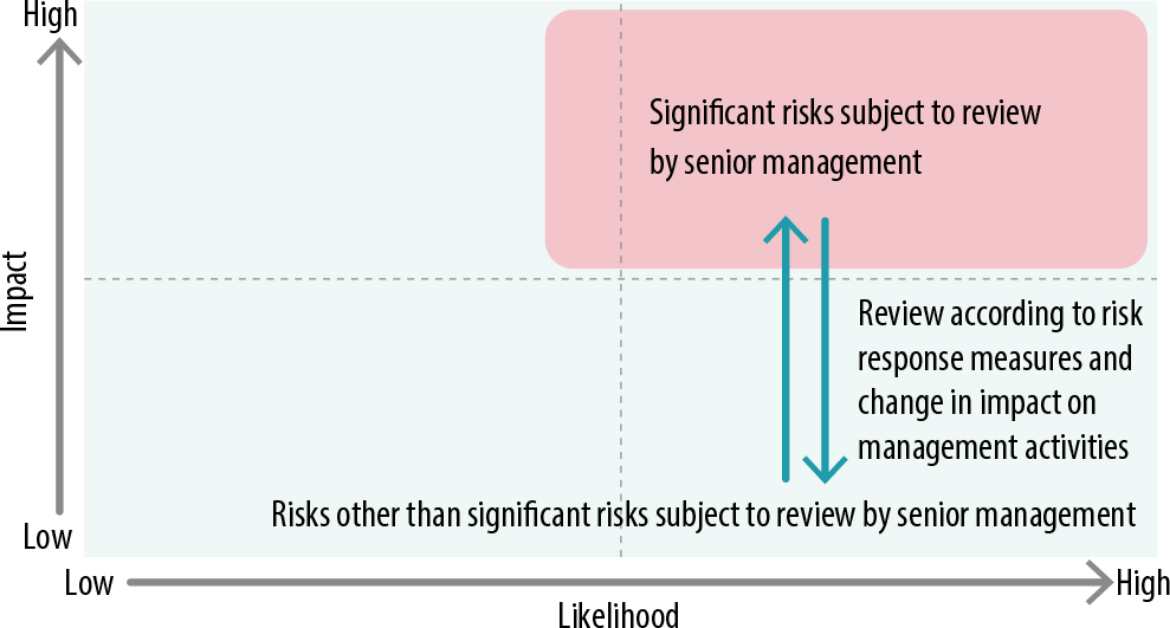
Among operational risks, risks that have a high impact on management activities and a high frequency of risk occurrence are identified as significant risks subject to review by senior management.
The Risk Management Committee, the Leadership Panel, and the Board of Directors meet quarterly to discuss the amount of integrated risk as well as policies and specific measures to address these significant risks subject to review by senior management in particular.
Risk Heat Map
Evaluation of Financial Soundness
In our evaluation of financial soundness, we use the rating methodologies of rating agencies to evaluate the long-term outlook for financial rating levels in the business planning workflow and implement balance sheet management to maintain a financial rating of A through FY2035.
Evaluation of Individual Investments
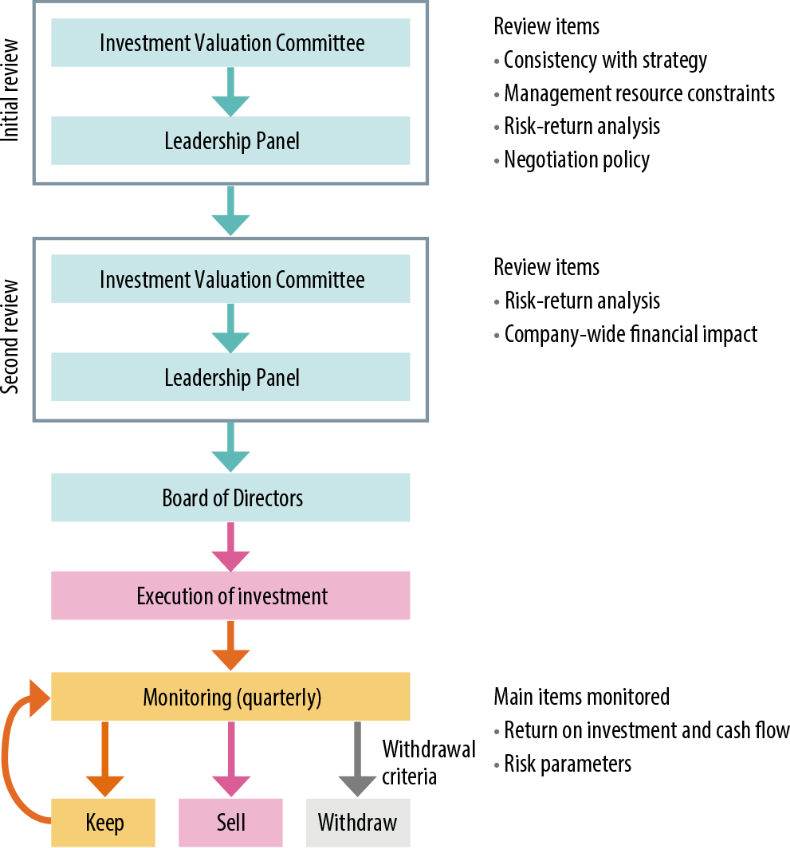
After confirming the consistency of individual investment evaluations with our field-specific investment strategies, our Investment Valuation Committee, which includes members with experience in investment screening at financial institutions and other organizations, conducts reviews by which we verify the long-term investment potential.
In addition, we properly evaluate and manage risks by engaging in regular monitoring and establishing withdrawal criteria.
Our risk-return analysis utilizes more than 200 guideline rates calculated for each strategic target country and business.
Investment Valuation Process
Countermeasures for Large-Scale Disasters
We have the largest power generation capacity in Japan. Based on the Basic Act on Disaster Management, we have put together and published our Operational Disaster Risk Reduction Plan, Operational Plan for the Protection of Citizens, and Operational Plan for COVID-19 and Other Pandemic Countermeasures. We also have emergency and disaster response rules and manuals in place to enable prompt decision-making and a swift response in the event of an emergency.
Recently, there has been concern regarding natural disasters such as earthquakes occurring directly beneath the Tokyo metropolitan area or off the Nankai Trough and an eruption of Mt. Fuji, which has prompted revisions by the national and local governments to damage estimates and disaster risk reduction measures. In light of these revisions, we are undertaking the necessary measures, such as earthquake-proofing our facilities in addition to periodically conducting drills to simulate large-scale disasters.
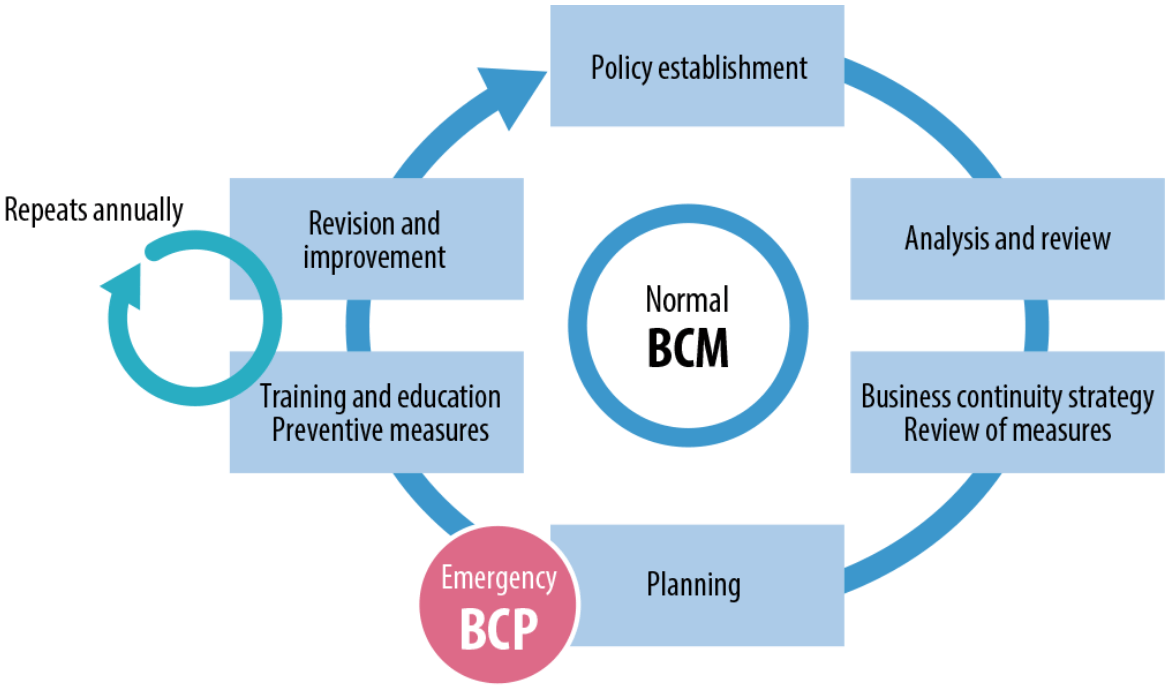
Enhancement of JERA’s BCP and BCM
Based on these rules, we have established the BCM Subcommittee, which reports to the Risk Management Committee regarding the establishment and review of the Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and regularly checks progress on disaster drills and advance measures.
In July 2023, under the scrutiny of outside experts, we received resilience certification for our BCP/BCM.

Basic Policy for JERA’s BCP and BCM
- In the event of any disaster or risk event, we will place the highest priority on the safety and security of people and ensure public safety in compliance with laws and regulations.
- To fulfill our responsibility as an energy provider supporting the social infrastructure in Japan, we will contribute to society and local communities by quickly restoring and continuing our core business of supplying them with electricity and gas.
JERA’s BCP and BCM Cycle
Enhancing Execution through BCP Drills
We also conduct rigorous drills under harsh conditions, including communication drills with shareholder companies, ship deployment exercises in the event of transportation disruptions, and satellite phone drills in the event of communication outages, all with the aim of enhancing our execution abilities. We will continue to strengthen our coordination with grid operators in the event of a supply-demand crunch.
Insights and challenges identified during these drills are continuously reviewed and improved upon, ensuring that we continue to work to further improve execution.

In-House BCP Drills
Featured
Creating the "Employee Action Guidelines" and the "JERA Disaster Prevention Guide for Families" in Case of Emergencies
The "Employee Action Guidelines for Emergency Disasters" were created to clearly outline the actions employees should take in the event of an emergency or disaster. It is designed to ensure their safety and the smooth and appropriate execution of disaster response. In addition to previously established guidelines for commuting employees, we have created new protocols for employees on business trips and those working from home.
Moreover, driven by the belief that protecting not just our employees but also their families is essential for employees to focus on disaster recovery, we have developed the "JERA Disaster Prevention Guide for Families." This guide provides easy-to-understand disaster preparedness measures for families who might need to remain at home during natural disasters such as earthquakes.
We are committed to the constant challenge of implementing initiatives that ensure safety is our top priority in emergencies.

Development and Ownership of Thermal Power Sources
As an electric utility provider, we believe that we need to ensure that our strategies are flexible and resilient, with options for responding to changes anticipated in the global business environment in the face of future uncertainties.
In developing plans for the development of new power sources and the retention of existing power sources, we set multiple scenarios for future power market conditions, including risk cases in which business opportunities for thermal power sources are reduced.
While taking into account future electricity demand and price competitiveness in the electricity market, we are replacing aging existing facilities with state-of-the-art, high-efficiency facilities in order to maximize earnings and avoid developing and owning unprofitable thermal power sources (so-called stranded assets).

