EnvironmentSustainability

Issue Awareness
As the world's population grows and the global economy develops, we see increasingly severe environmental issues on a global scale, including overuse of resources, waste and pollution, and loss of biodiversity. Global warming, in particular, is progressing due to increased greenhouse gas emissions from human activities, and disasters caused by extreme weather events are becoming more frequent and intense worldwide, threatening people’s livelihoods and economic activities.
Amid this situation and in response to the agreements by the international community on SDGs and the Paris Agreement, the development of targets and frameworks for climate change countermeasures, conservation of biodiversity, and the creation of a recycling-oriented society is accelerating. As such, there are increasing demands and expectations for governments and corporations to take action.
Fundamental Approach on Environment
We are committed to taking the initiative in working to solve environmental issues while coordinating with our stakeholders by utilizing our technologies and know-how to realize a sustainable society that works for the environment and the economy.
As a leader in the domestic thermal power generation industry, we respect energy and environmental policies such as the Basic Energy Plan and proactively promote renewable energy development.
In addition, as we seek to become a global energy company, we comply with the environmental laws and regulations of each country and region in our various business activities, fully recognizing the need to protect the environment on a global scale. This involves not only improving power generation efficiency, reducing CO2 emissions, preventing air and water pollution, and recycle waste but also striving for biodiversity conservation to realize a sustainable environment, society, and economy.
Environmental Management System
We have also established a Sustainability Promotion Committee to improve our ESG management. Chaired by the President, Director, CEO and COO, this cross functional committee oversees the entire company and examines environment related issues and their corresponding measures, with significant issues brought to the Leadership Panel for resolution. and, if necessary, to the Board of Directors for resolution. We will continue to improve our management of the environment and contribute to the development of a sustainable society.
Environmental Education
We provide training for employees involved in environmental operations at our power plants and other facilities. This enables them to acquire the necessary knowledge and skills concerning the environment, helping our employees to understand the impact of our business activities on the environment. Training levels correspond to job class and proficiency, and we are working to develop environmental education programs for employees.
Material Balance (FY2023*)
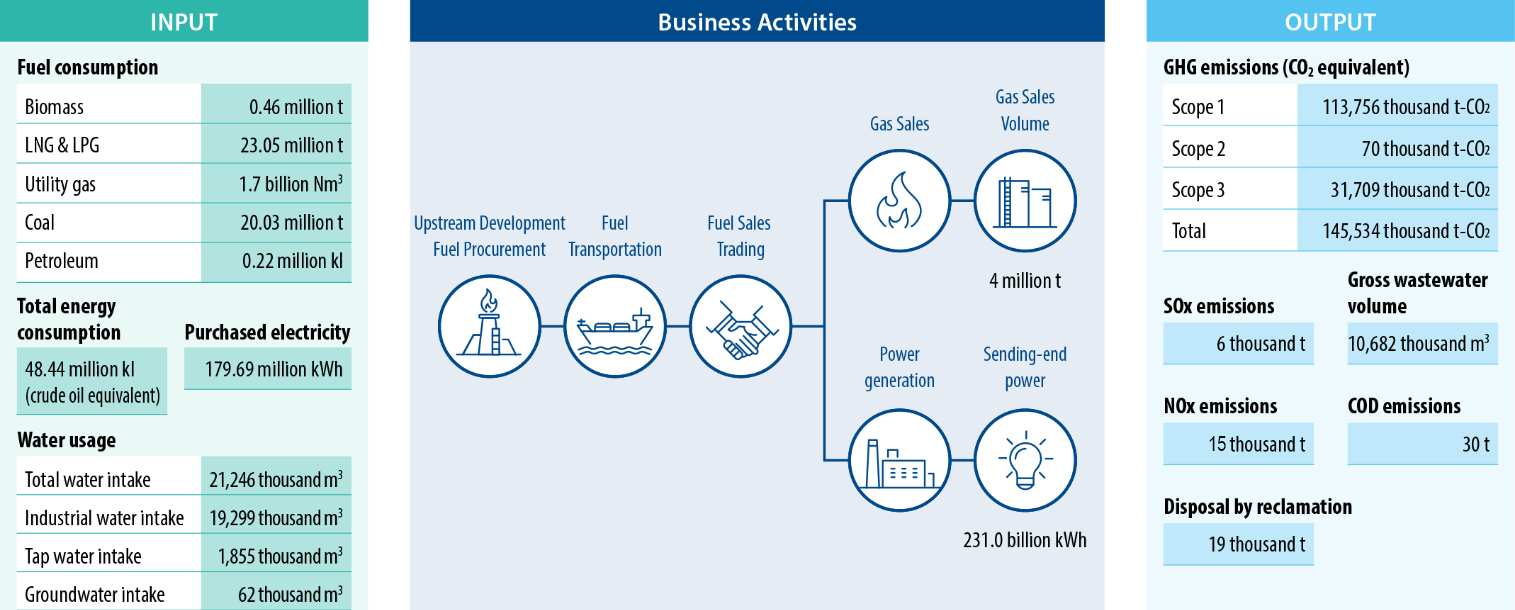
- Figures for JERA operations in Japan and joint ventures with Hitachinaka Generation Co., Inc., JERA Power TAKETOYO LLC., JERA Power YOKOSUKA LLC., and JERA Power ANEGASAKI LLC., Green Power Ishikari GK.
Featured
Independent Assurance on Environmental Data
To improve the credibility of our environmental data, starting with values reported for FY2021, we have received independent third-party assurance from KPMG AZSA Sustainability Co., Ltd. for certain environmental data, including GHG emissions, which is available on our corporate website.
Participation in the GX League

Green transformation (GX) refers to the transformation of the entire economic and social system to achieve emission reductions and increase industrial competitiveness by viewing initiatives to achieve greenhouse gas reduction targets as an opportunity for economic growth.
In line with our mission to provide cutting edge solutions to the world’s energy issues, we have announced our target of JERA Zero CO2 Emissions 2050 and are committed to achieving net zero CO2 emissions from our operations in Japan and abroad by the year 2050. We believe that our efforts align with the objectives of the GX League and have continued our involvement, announcing our formal participation in the league following our endorsement of the GX League Basic Concept in 2022.
We will continue to take the lead in the decarbonization of the energy industry by proactively developing decarbonization technologies and by working with related institutions, organizations, and stakeholders to resolve various issues.
Fundamental Approach on Preserving Biodiversity
As a leader in the domestic thermal power generation industry, we respect the energy and environmental policies represented by the Strategic Energy Plan and recognize the importance of biodiversity conservation, such as the 30 by 30*1 initiative to halt the loss of international biodiversity and put it on a recovery track (nature positive). We will conduct our business activities in compliance with environmental impact assessments, regional agreements, environmental laws and regulations, and other relevant laws and regulations.
In Japan, when endangered plants and animals are identified in the environmental impact assessment of our own and SPC power plants, we take steps to preserve biodiversity, including efforts to maintain and restore habitats and ecosystems. For example, The environmental impact assessment conducted when replacing the Yokosuka Thermal Power Station (Units 1 and 2) showed that the area was inhabited by falcons, which are designated as a rare endangered species in Japan. Accordingly, we have taken measures to avoid affecting their habitat, which included using low-noise, low-vibration machinery during construction. We’ve also installed nesting boxes for falcons in our stacks to create an environment conducive to nesting. We will continue our efforts to preserve the habitat by maintaining green areas.
Chita Thermal Power Station is also participating in the “Project Linking Life with One Another” by the non-profit Japan Ecologist Support Association. We view the coastal environment of the Chita Peninsula as a single ecosystem, and in collaboration with other businesses, local governments, experts, non-profit organizations, and students, we are working to enhance biodiversity and establish an ecological network, which is recognized as a Chita Peninsula Green Belt, a nature symbiosis site*2 .
- 1 30 by 30 is a goal to effectively conserve at least 30% of land and sea as healthy ecosystems by 2030, with the goal of halting and restoring biodiversity loss by 2030 (nature positive). The goal was agreed at the G7 Summit in 2021.
- 2 https://policies.env.go.jp/nature/biodiversity/30by30alliance/documents/nintei/R5Early44_Chita_Peninsula_Green_Belt.pdf(Japanese only)

