Naming Ceremony Held for Japan’s First LNG Bunkering Vessel2020/09/18
On September 16, a naming ceremony was held at the Sakaide Works of Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. for Japan’s first LNG bunkering vessel (“LBV”).
The ceremony was attended by Masashi Asakura, Chief Officer for Production Group of Toyota Motor Corporation (head office: Toyota city, Aichi prefecture; President: Akio Toyoda); Masahiro Kato, Deputy Director-General for Engineering Affairs, Ports and Harbors Bureau of Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism; and a number of related parties.
LBV was named “Kaguya” by Yukikazu Myochin, President of Kawasaki Kisen Kaisha, Ltd. (“K-Line”), and Hitoshi Nagasawa, President of Nippon Yusen Kabushiki Kaisha (“NYK”), and the ceremonial rope holding LBV in place was cut by Sunao Nakamura, Managing Executive Officer of JERA Co., Inc. (“JERA”) , and Toshiro Hidaka, CEO for Machinery, Energy & Project Division of Toyota Tsusho Corporation (“Toyota Tsusho”).
LBV's name, Kaguya, derives from Princess Kaguya in "The Tale of the Bamboo Cutter," which is said to be Japan's oldest story and is still loved by many people today. The name also expresses our desire to grow the LNG bunkering market as long and high as a bamboo tree.
Kaguya is the first LNG bunkering vessel to be operated in Japan. Kaguya will be operated by Central LNG Marine Fuel Japan Corporation and will be based at JERA's Kawagoe Thermal Power Station. Kaguya will begin supplying LNG fuel* to ships in the Chubu region in October or later this year using Ship-to-Ship bunkering.**
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has agreed on a goal to reduce GHG emissions from shipping by at least 50 percent by 2050 compared to 2008, and the delivery of LNG-fueled ships is expected in the future. After the start of operation, Kaguya will supply LNG to Sakura Leader, which is the first large LNG-fueled PCTC (pure car and truck carrier) operated by NYK, and to a new car carrier to be delivered by K-Line this fiscal year, as well as to other LNG-fueled vessels.
The expertise and strengths of each company — including K-Line's technological expertise accumulated through its long-term LNG carrier operations, JERA's operational and technical capabilities at its large-scale terminals, Toyota Tsusho's global sales network for marine fuel, and NYK's experience in the world's first LNG fuel supply and sales business — will be utilized to provide LNG bunkering in Japan’s Chubu region and expand our marketing services to promote the use of LNG as a fuel for ships, thereby contributing to a reduction of our environmental impact.
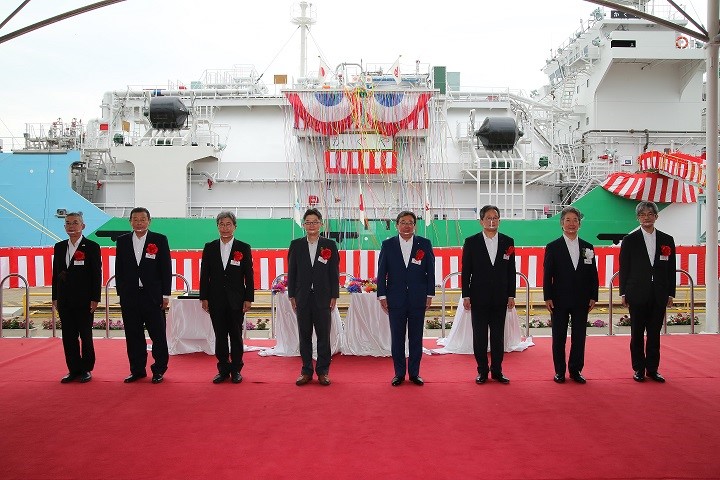

From left)
Masahiro Uesono, Director of Shikoku District Transport Bureau
Masashi Asakura, Chief Officer for Production Group of Toyota Motor Corporation
Toshiro Hidaka, CEO for Machinery, Energy & Project Division of Toyota Tsusho Corporation
Sunao Nakamura, Managing Executive Officer of JERA Co., Inc.
Hitoshi Nagasawa, President of Nippon Yusen Kabushiki Kaisha
Yukikazu Myochin, President of Kawasaki Kisen Kaisha, Ltd.
Hashimoto Yasuhiko, President and Chief Executive Officer of Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Masahiro Kato, Deputy Director-General for Engineering Affairs, Ports and Harbors Bureau of Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
<Principal Particulars of LBV>
LNG cargo tank capacity: 3,500 m3
Gross tonnage: 4,044 tons
Length overall: 81.7 m
Breadth: 18.0 m
Shipyard: Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. ,Sakaide Works
<Supply Chain>
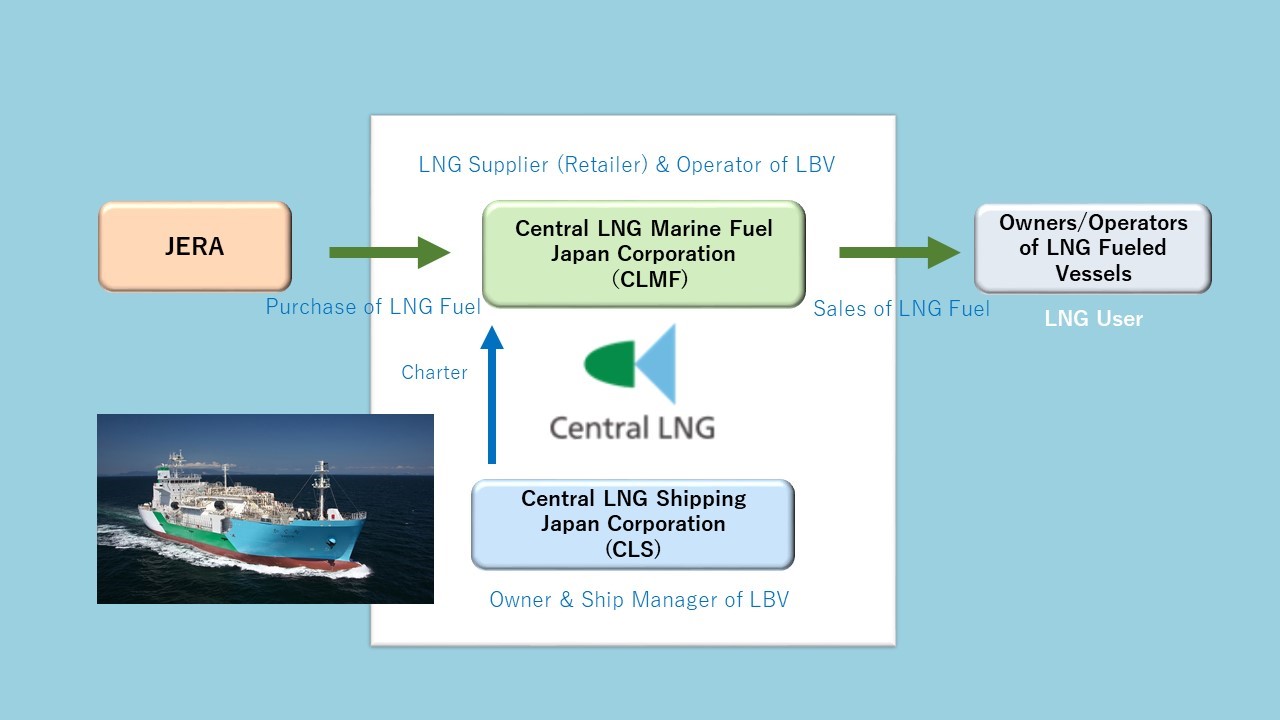
For more information about Central LNG Marine Fuel Japan Corporation and Central LNG Shipping Japan Corporation, please visit the following website:
* Merits of LNG
Compared to heavy fuel oil, the use of LNG can reduce emissions of sulfur oxides (SOx) and particulate matter (PM) by approximately 100%, nitrogen oxides (NOx) by as much as 80%, and carbon dioxide (CO2) by approximately 30%.
** Ship-to-Ship Bunkering
A method of bunkering where an LNG bunkering vessel comes alongside an LNG-fueled vessel to supply LNG at different locations such as along the quay or pier or at anchor.

